Streaming Data Pipeline with Amazon S3, SQS, and CocoIndex for Real-Time Processing
CocoIndex https://github.com/cocoindex-io/cocoindex now natively supports Amazon S3 as a data source, allowing seamless integration with your storage. Combined with support for AWS Simple Queue Service (SQS), CocoIndex enables true real-time, incremental processing of data as it's updated in S3.
Why Choose Incremental Processing?
Incremental processing focuses on handling only the new or modified data since the previous run, rather than reprocessing the entire dataset every time. This method becomes essential when working with large-scale data or when up-to-date information is critical.
When Incremental Processing Matters
1. Freshness is Critical
In user-facing applications, data freshness is non-negotiable. For instance, if a user edits a document, they expect those changes to be instantly reflected in search results. Delays can result in outdated information being surfaced. If this data is used by AI systems—like language models—it could lead to incorrect or misleading responses. Worse, users may not realize the information is outdated, increasing the risk of misuse.
2. Expensive Transformations
Some processing tasks, especially those involving complex transformations or AI models like embeddings or large-scale inference, are computationally intensive. Repeating these tasks unnecessarily for unchanged data is wasteful and costly.
3. Working at Scale
Large datasets pose significant challenges in terms of compute, time, cost, and storage. If your data lives in Amazon S3 and spans terabytes, reprocessing the entire set for every small update is neither efficient nor sustainable. Incremental processing enables scalable workflows by focusing only on what's changed.
In short, if T is your tolerance for data staleness, and full reprocessing every T interval isn’t feasible, incremental processing becomes the practical and scalable path forward.
Technical Benefits of CocoIndex's Incremental Processing
Optimized Resource Utilization
CocoIndex processes only the S3 files that have been newly added or updated, reducing unnecessary compute cycles and improving overall system efficiency.
Seamless Real-Time Updates via SQS
By integrating with AWS Simple Queue Service (SQS), CocoIndex reacts instantly to changes in your S3 bucket, enabling near real-time data transformation without polling delays.
Built-In Data Integrity & Lineage Tracking
CocoIndex maintains a persistent state of previously processed data, ensuring consistent outputs across runs. It also tracks data lineage to provide full visibility into how each piece of data was transformed.
Granular Smart Caching
Performance is further enhanced by an intelligent caching mechanism that operates at a fine-grained level. Instead of reprocessing entire files, CocoIndex selectively recomputes only the altered portions—such as individual data chunks—based on transformation logic. For example, if only a few of M chunks in a file are modified, only those changed chunks are re-embedded, saving both time and compute.
AWS SQS
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) is a fully managed message queuing service that enables you to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications. It provides a reliable, highly-scalable hosted queue for storing messages as they travel between applications or microservices.
When files are uploaded to or modified in S3, SQS receives notifications about these changes and queues them as messages. Each message contains metadata about the S3 event, such as:
The type of event (e.g., ObjectCreated, ObjectRemoved)
The S3 bucket name
The object key (file path)
Timestamp of the event
Other relevant metadata
These messages remain in the queue until they are successfully processed, ensuring no events are lost even if the processing system is temporarily unavailable.
Live update out of the box with SQS
CocoIndex provides two modes to run your pipeline, one time update and live update, both leverage the incremental processing. Particularly with AWS SQS, you could leverage the live update mode - where CocoIndex continuously monitors and reacts to the events in SQS, updating the target data in real-time. This is ideal for use cases where data freshness is critical.
How does it work?
Let's take a look at simple example of how to build a real-time data transformation pipeline with S3 and CocoIndex. It builds a vector database of text embeddings from markdown files in S3. You could find a similar example to process local files in this blog.
S3 bucket and SQS setup
Please follow the documentation here to setup S3 bucket and SQS queue.
S3 bucket
Creating an AWS account.
Configuring IAM permissions.
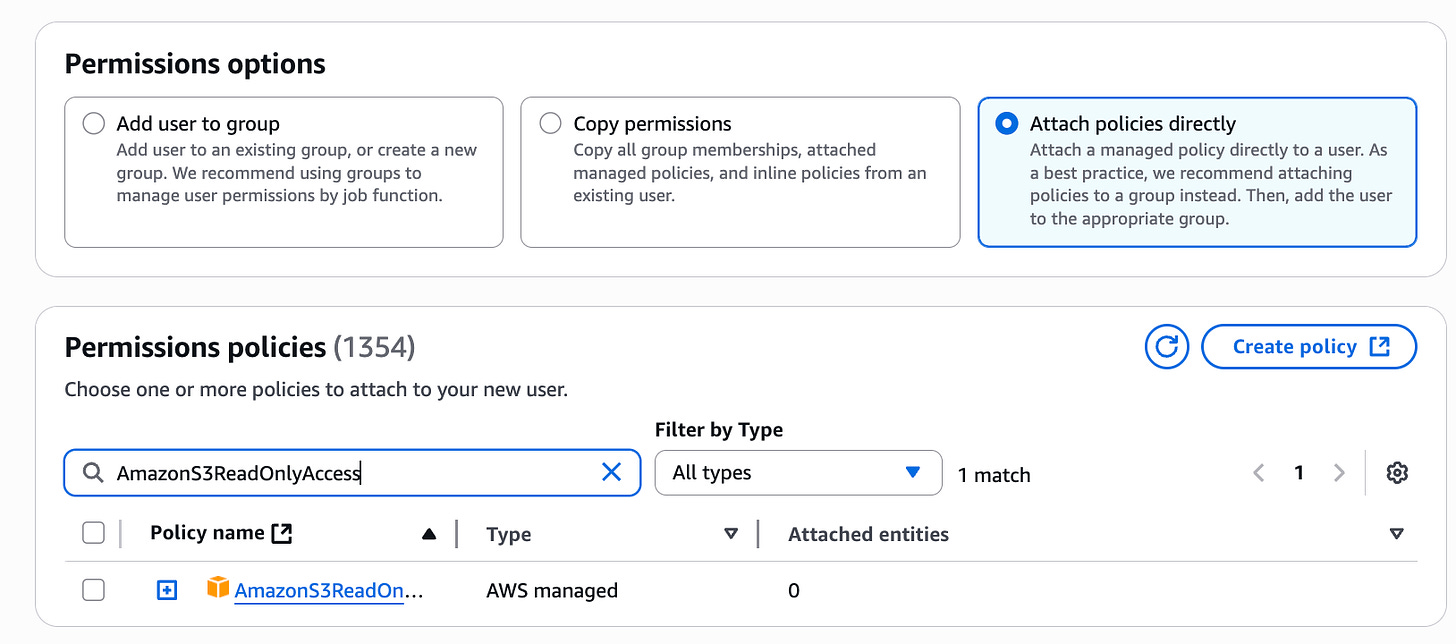
Configure policies. You'll need at least the
AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccesspolicy, and if you want to enable change notifications, you'll also need theAmazonSQSFullAccesspolicy.
SQS queue
For real-time change detection, you'll need to create an SQS queue and configure it to receive notifications from your S3 bucket. Please follow the documentation to configure the S3 bucket to send event notifications to the SQS queue. Particularly, the SQS queue needs a specific access policy that allows S3 to send messages to it.
{
...
"Statement": [
...
{
"Sid": "__publish_statement",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "s3.amazonaws.com"
},
"Resource": "${SQS_QUEUE_ARN}",
"Action": "SQS:SendMessage",
"Condition": {
"ArnLike": {
"aws:SourceArn": "${S3_BUCKET_ARN}"
}
}
}
]
}
Then you can upload your files to the S3 bucket.
Define Indexing Flow
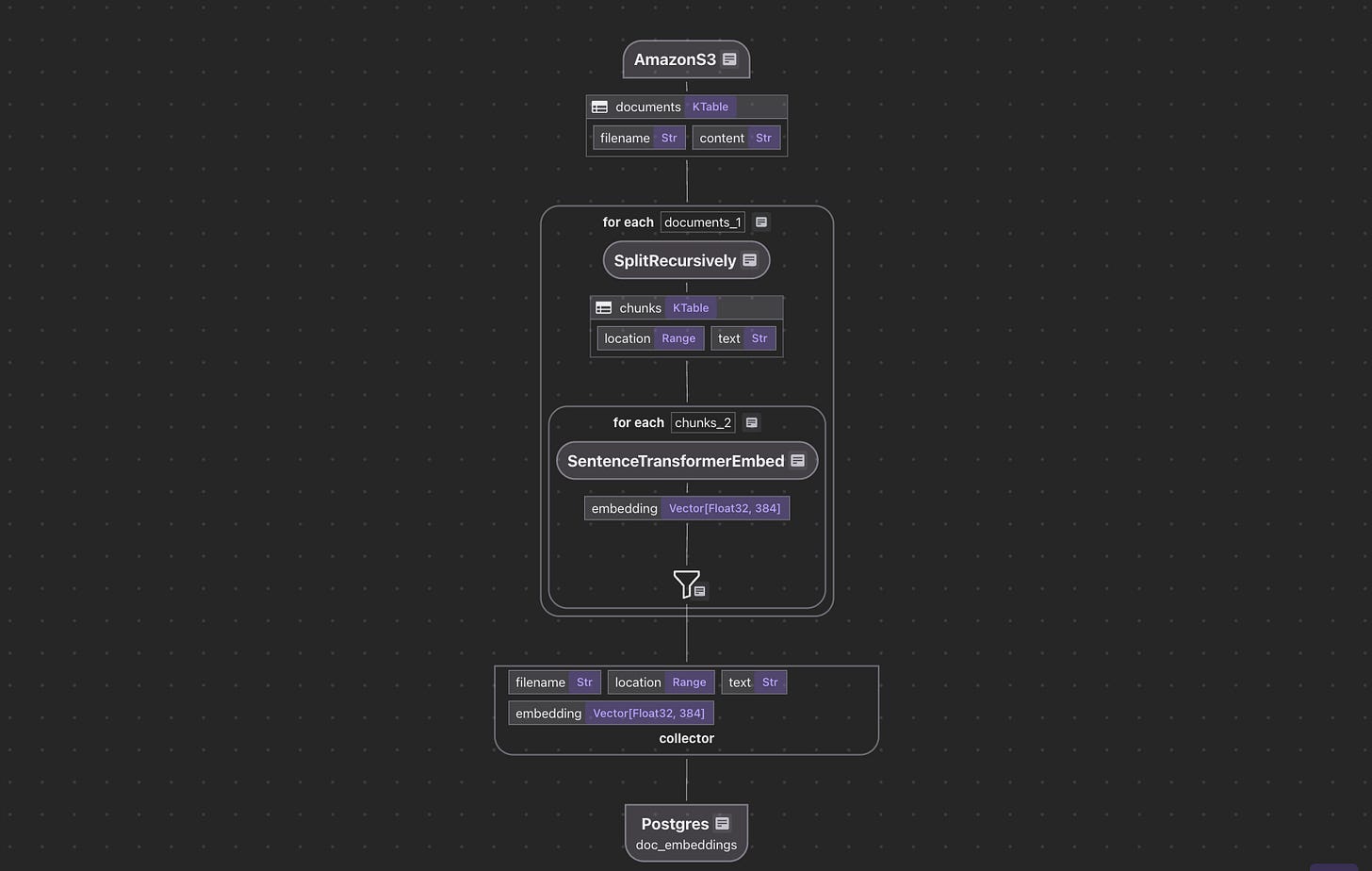
Flow Design
The flow diagram illustrates how we'll process our codebase:
Read text files from the Amazon S3 bucket
Chunk each document
For each chunk, embed it with a text embedding model
Store the embeddings in a vector database for retrieval
AWS File Ingestion
Define the AWS endpoint and the SQS queue name in .env file:
# Database Configuration
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://localhost:5432/cocoindex
# Amazon S3 Configuration
AMAZON_S3_BUCKET_NAME=your-bucket-name
AMAZON_S3-SQS_QUEUE_URL=https://sqs.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/123456789/S3ChangeNotifications
Define indexing flow and ingest from Amazon S3 SQS queue:
@cocoindex.flow_def(name="AmazonS3TextEmbedding")
def amazon_s3_text_embedding_flow(
flow_builder: cocoindex.FlowBuilder, data_scope: cocoindex.DataScope
):
bucket_name = os.environ["AMAZON_S3_BUCKET_NAME"]
prefix = os.environ.get("AMAZON_S3_PREFIX", None)
sqs_queue_url = os.environ.get("AMAZON_S3_SQS_QUEUE_URL", None)
data_scope["documents"] = flow_builder.add_source(
cocoindex.sources.AmazonS3(
bucket_name=bucket_name,
prefix=prefix,
included_patterns=["*.md", "*.mdx", "*.txt", "*.docx"],
binary=False,
sqs_queue_url=sqs_queue_url,
)
)
This defines a flow that reads text files from the Amazon S3 bucket.
Rest of the flow
For the rest of the flow, we can follow the tutorial in this blog. The entire project is available here.
Run the flow with live update
cocoindex update main.py -L
-L option means live update, see the documentation for more details. And you will have a continuous long running process that will update the vector database with any updates in the S3 bucket.
If you need to run the server and indexing in the same process, without spawning two separate jobs, you can add the FlowLiveUpdater in the main() function, see the example here. And you can run the server with python3 main.py.
Support us
We are constantly improving, and more features and examples are coming soon. If you love this article, please give us a star ⭐ at GitHub to help us grow.
Thanks for reading!